In an earlier post I mentioned work I was doing to show the importance of tone in the Bantu D30 languages. Here I’d like to go through the conjugation of one verb in one language, to show how tone works, in relationship to consonants and vowels. To start with, here is one verb conjugated two ways:
If you have studied another language before, you might recognize this kind of listing of the forms of a verb for each of the people who do the action. In English, this kind of thing is boring:
- I walk
- you walk
- he walks
- we walk
- you all walk
- they walk
The only thing of any interest in the English is the final ‘s’ on ‘he walks‘; everything else is the same on the verb. But that’s not the case in many languages, including the languages I’m working with. For instance, there are lots of differences in forms, and you can correlate the differences in forms with differences in meaning. If you line up the verbs as below, you can separate the part that remains the same from the part that changes. You can also notice that in the meanings on the right, there is a part that remains the same, and a part that changes. This is the case for both conjugations:

So with a conjugation paradigm like this, we can deduce that for each line in the paradigm, the part of the form that is different is related to the part of the meaning that is different (e.g., k- = “we” and ɓ- = “they”). Likewise, the part of the word forms that stays the same is related to the part of the meaning that stays the same (e.g., otoko = “will spit”).
But, you might ask, this logic gives us otoko = “(did/have) spit” in the first conjugation, but otoko = “will spit” in the second. Which is it? In fact, if you compare each line for each of the two conjugations, you will see that the consonants and vowels are the same for each first line, for each second line, all the way down to the sixth line. So whatever form indicates the difference between “will” and “did/have” is not found in the consonants or vowels. Where is that difference indicated? In the tone. If you compare the second column for each line of the two conjugations, you will see that the lines representing pitch for each word form is not the same between the two conjugations.
A similar problem exists for the prefixes that refer to subjects. That is n- is used for both “I” and “you all”, and the absence of a prefix is used for both “you” and “he”. But looking at this last one first, we can see a difference in the tone: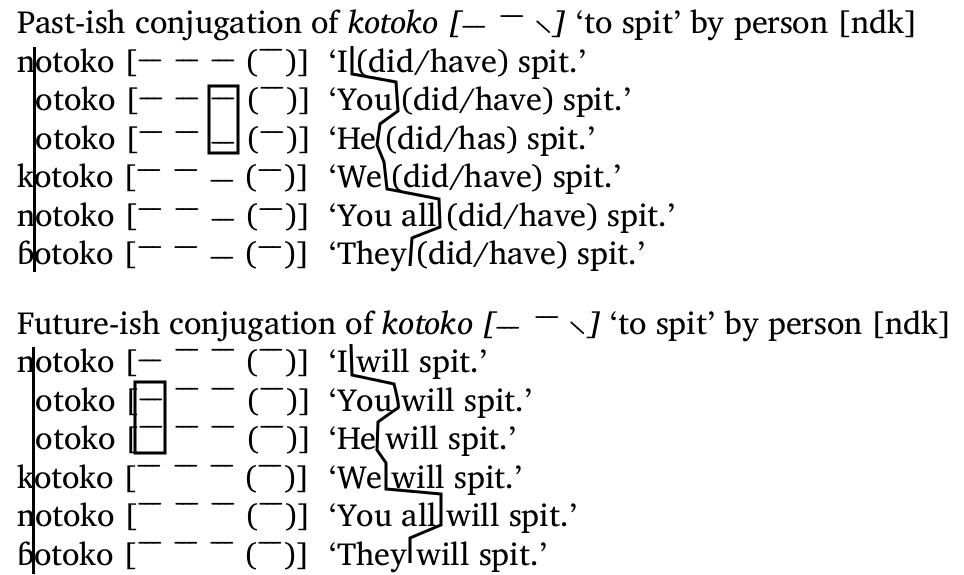
So even though there is no difference in the consonants or vowels to indicate a difference in meaning, there is a difference in tone which does. The same is found for “I” versus “you all”, circled here:
So the bottom line is that for (almost) every difference in meaning, there is a difference in form that indicates that difference. Sometimes that difference is in the consonants or vowels, as we might expect in languages more closely related to English (and even in English, with the -s above), but sometimes that difference is only in the tone.
But the story is a bit more complex than that, since the tone doesn’t do just one thing. We saw above that tone indicates the difference between “will” and “did/have” in these conjugations. But tone also indicates the difference between c, as well as that between “I” and “you all”. That means “you will”, “you did”, “he will”, and “he did” all have the same consonants and vowels, and are only distinguished one from another by the tone. And there’s another quadruplet with “I” and “you all”, and these quadruplets exist for almost every verb in the language: this is a systematic thing.
So with two minimal quadruplets for each verb in the language, it makes sense to ask what is the contribution from each meaningful word part to the tone, and how they come together. For instance, what is the contribution of “you”, as opposed to “he”, on the one hand, and what is the contribution of “will”, as opposed to “did/have”, on the other? And how to these different bits of tonal information combine to form the tone patterns we hear on full words? (Hint: they are a lot harder to chop up than the consonant prefixes above).
Anyway, that’s the essence of what I do, in brief. By looking at the actual pronunciations of words in a system, we can deduce what the contribution of each meaningful word part is, then make hypotheses about how they come together, and test those hypotheses until we come up with a coherent system.
